Do You Have A Labral Tear In Your Hip?
If you have a labral tear in your hip, you may wonder what treatment options are available. Can exercises help, or will you need a surgery to repair your labrum? And if so, how long does it take to recover?
Watch the video to learn the answers to those questions, plus more information about labral tears in the hip.

What Is A Labral Tear In Hip?
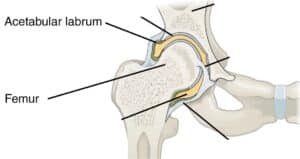
What Is The Hip Labrum?
The hip joint is the meeting point between the pelvis and the thigh bone (femur).
The joint itself is a ball-and-socket joint between the femoral head (ball) and the acetabulum (socket).
The hip labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the outside of the socket.
What is the function of the hip labrum?
The function of the hip labrum is to deepen the hip soceket and make the hip joint more stable as well as to disperse forces created during movement.
Labral Tear In Hip
A labral tear in the hip happens when the labrum tears. This can cause instability in the hip as well as an increased risk for hip arthritis in the future.
What Causes A Labral Tear In Hip?
The main causes of labral tears in the hip are:
- Trauma
- Structural abnormalities
- Repetitive motions
- Degenerative changes over time
Traumatic Hip Labral Tears
Traumatic injuries to the hip labrum often occur after a hip dislocation. Such an injury may result from a car accident or high-impact contract sports like ice hockey, football, and soccer. When this happens, you'll usually notice symptoms right away.
Structural Abnormalities
Structural dysfunction refers to the innate structural differences in hip joint anatomy. Some people are born genetic hip issues such as hip dysplasia that can make the hip joint inherently unstable. Many children born with hip dysplasia have difficulty with their hips early in life that can affect them throughout their lives. However, with proper early treatment including physical therapy, many children with hip dysplasia can enjoy happy, active lives.
Other hip joint abnormalities that can lead to labral tears include a shallow acetabulum (hip socket) that does not sufficiently cover the femoral head. This makes the hip joint more reliant on the labrum for stability.
Contrarily, an acetabulum (socket) that hangs over the femoral head (ball) too much can also put you at risk for labral tear. This is referred to as a pincer-type femoroacetabular impingement. The socket impinges on the hip joint and can lead to a tear of the labrum.
Repetitive Motions
Repetitive motions such as participation long-distance running or sports that require repetitive twisting or pivoting such as golf can wear down the labrum over time and lead to a labral tear.
Degenerative Changes
Degenerative joint dysfunction, such as osteoarthritis, is a chronic condition that slowly degrades the cartilage in the hip joint. As the cartilage degrades, there is an increased likelihood of cartilage tearing. Risk factors of osteoarthritis are older age and/or increased weight.
Hip Labral Tear Symptoms
Hip labral tear symptoms can vary from person to person depending on the location and size of the tear.
Some people may not experience any symptoms at all. In fact, many people with a labral tear in their hip can continue to exercise and play sports without pain and without their performance suffering.
On the other hand, other people with a hip labral tear may experience symptoms such as:
- Pain in the groin or buttock
- Hip stiffness or lack of mobility
- Catching, clicking, or locking sensations during movement
- A feeling of unsteadiness or instability in their hip
- Discomfort during prolonged static positions such as sitting or standing
- Pain with prolonged activity such as walking or running
Do I Need An MRI To Diagnose A Labral Tear In My Hip?
A labral tear is usually diagnosed with a physical examination that includes different movement tests to determine the specific source of the pain.
Imaging such as an MRI can help with confirming a diagnosis as well as determining the location and severity of the tear.
However, you probably don't need an MRI of your hip unless you're planning on having labral tear surgery.
Why is that?
Many people with a labral tear in their hip will get better with non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy.
The physical therapy treatment for a hip labral tear won't change by knowing the exact size or location of the tear, or even if whether or not there's definitively a labral tear at all.
The physical therapy treatment of a labral tear is dependent on your clinical exam, your motion and strength limitations, and the specific movements that aggravate your symptoms.
Therefore, you can have an MRI of your hip if you need the peace of mind of knowing that you do or do not have a labral tear. However, it's likely to just be an expensive test that doesn't affect your treatment unless you're considering surgery.
Treatment For Labral Tear In Hip
Will I need surgery for a labral tear in my hip?
The true and honest answer is: Maybe.
A hip labral tear does not heal on its own.
However, smaller tears can be managed conservatively with physical therapy.
Although I'm not a huge fan of unnecessary cortisone injections, intra-articular (inside the joint) problems such as a labral tear are one instance where judicious use of cortisone or other steroid injections can help "calm down" the symptoms while you address the root cause with physical therapy.
Want To Discover The Root Cause Of Your Hip Pain?
Tap the button below to request a Free Discovery Visit with one of our specialist physical therapists.
Labral Tear Hip Surgery
For more severe labral tears, or if symptoms persist after six to eight weeks of conservative treatment, surgery may be recommended.
Most labral tears in hip are addressed arthroscopically where the surgeon makes small cuts in the hip and uses small instruments to fix the tear and the surrounding tissues.
After surgery, physical therapy is needed address the strength and flexibility deficits in the hip and help you progress back into activity safely.
Full recovery after a labral tear hip surgery usually takes four to six months depending on the level of activity that you're trying to get back to.
If you do decide to have surgery, be prepared for that!
Surgery isn't a quick fix for a labral tear in the hip, and often times it can be avoided.
Can A Brace Help A Labral Tear In The Hip?
A small randomized-controlled trial showed some favor for hip unloader braces in patients with femoroacetabular impingement and hip labral tears.
The results are still not definitive but if you're looking to relieve hip pain and avoid labral tear surgery, a hip brace might be worth trying.
Exercises For Labral Tear In Hip
Can exercises really help a labral tear in the hip?
Many people wonder how doing exercises can help a labral tear.
"How will exercises fix my labral tear?"
And the honest answer is that exercise don't make the labrum heal.
What exercises ARE able to do to help a hip labrum tear are to:
- Improve the movement of the hip joint so that you don't keep pinching (read "further injuring") your labrum.
- Strengthen the muscles that stabilize the hip to make up for the instability caused by a labral tear.
What Are The Best Exercises For A Hip Labral Tear?
As mentioned above, exercises for a labral tear in the hip should focus on improving mobility of the hip joint and stabilizing the ball in the socket.
Stretching Exercises For Labral Tear In Hip
Posterior pelvic tilt
If the acetabulum (hip socket) overhangs the ball too much, this can pinch the labrum as you move your hip.
Tilting your pelvis backwards, as if lifting your belt buckle up toward the ceiling can increase the amount of space in the hip joint if you have a pincer-type impingement of the hip.
This exercise is also very helpful if your back hurts from standing too long.
All 4's Rocking
Rocking on your hands and knees (the "child's pose") is a common yoga pose used for lower back pain.
It can also be used effectively to help improve hip joint mobility so that you don't pinch you labrum.
However, instead of allowing your lower back to round and stretching your lower back muscles, you want to keep your lower back in a neutral position or even a slight arch so that all of the rocking is coming from your hips joints
Learn variation of the all 4's rocking exercise for back and hip pain.
Hip Flexor Stretches
If your hip flexors are too stiff, they can tilt your pelvis forward and cause the same problem as standing with too much of a forward pelvic tilt.
Learn how to stretch your hip flexors here.
Hamstring Stretches
You wouldn't think your hamstrings would have a lot to do with labral tears.
After all, the hamstrings are in the back of your leg, and usually labral tears hurt in the front of the hip.
However, if you use your hamstrings too much because your gluteal muscles area weak, your hamstrings can get stiff and cause the ball of the hip to glide forward in the socket.
Additionally if both your hamstrings and hip flexors are stiff, this can create increased compression in the hip joint and can cause increased stress on the labrum.
Learn how to stretch your hamstrings here.
Strengthening Exercises For Labral Tear In Hip
Your gluteal muscles (butt muscles) are the stabilizing muscles in your hip. They're synonymous to the rotator cuff in your shoulder.
Your glutes function to hold the ball of your hip stabilized in the socket while also helping you keep your body balanced on one leg when standing and walking.
Clamshell Exercise
The clamshell exercise is one common way to strengthen your glute muscles. However, most people do it incorrectly. Learn how to do the clamshell exercise correctly here.
Additionally, the clamshell exercise is a very low-level exercise, and it's also not very functional.
After all, most people with labral tears in their hip have pain when they're on their feet standing and walking.
Therefore, if it's a good idea to do strengthening exercises for your hip in a standing position.
Single Leg Balance
Just standing on one leg is a good exercise to help you balance your body over your hip when walking.
As you get stronger though, you man want a more difficult exercise, especially if you want to get back to running without hip pain.
Single Leg Mini-squat
Doing single leg mini-squats is a great way to strengthen your glutes and mimics the motion of your hip when running or going up and down stairs.
Do this by first balancing on one leg and then slightly leaning forward and pushing your hips back so that your knee bends slightly.
You want to keep your weight on your heel and knee over toes in order to get the maximum benefits for your glutes.
How To Get Lasting Relief For A Labral Tear In Your Hip
The above exercises are a great starting point for strengthening the muscles around the hip joint.
However, just doing exercises may not necessarily address the root cause of the labral tear in your hip.
The big question is:
What caused the labral tear in your hip in the first place?
If you'd like discover what caused the labral tear in your hip and what you can do about it in order to prevent needing surgery, tap the button below to request a free discovery visit.
Like this post? See our other posts about hip pain
Such as:
Prevent hip pain when sleeping at night
Can't lift leg to get in the car?