Do You Have A Labral Tear In Your Shoulder?
Watch the video to learn the causes, symptoms, treatment, & exercises for a labral tear in your shoulder.

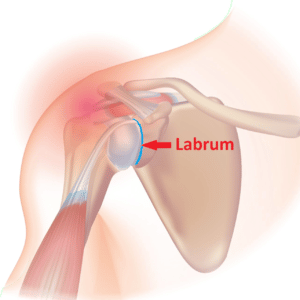
What Is The Shoulder Labrum?
The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint, kind of like a golf ball sitting on a golf tee.
The "socket" or "tee" part of the shoulder joint is called glenoid fossa, while the "ball" of the joint is called the humeral head.
The labrum surrounds the edge of the "tee" and helps deepen the socket
What Does The Labrum Do?
The function of the labrum is to help give the shoulder joint a little more stability.
The shoulder is a really mobile joint, which allows you to move your shoulder in all sort of motions such as:
- Reaching overhead into a cabinet
- Reaching behind your back
- Swinging a golf club
- Playing tennis or pickleball
- Swimming
However, in order to have this amount of mobility, the shoulder joint sacrifices stability.
The labrum deepens the "socket" of the glenoid fossa and allows your shoulder to stay in socket as you move your arm.
What Causes A Labral Tear In The Shoulder?
A labral tear in the shoulder can be caused in a few different ways:
- Trauma
- Overuse
- Degeneration over time
Types of Labral Tears In The Shoulder
Bankart Lesion of the Shoulder
The first type of labral tear in the shoulder is called a Bankart lesion.
This type of tear typically occurs in younger people who dislocate their shoulder for example during a fall or a sports injury.
Since the labrum normally increases stability of the shoulder, a Bankart lesion causes the shoulder to become unstable. In turn, there's a higher risk of dislocating the shoulder again.
The treatment for a Bankart lesion is often surgery, especially in active people less than 20 years of age.
SLAP Tear (Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior)
The second type is a SLAP tear. It stands for “Superior Labrum from Anterior to Posterior.”
- Superior - meaning "top"
- Labrum - it's a labral tear in the shoulder
- Anterior- front
- Posterior - back
Essentially, a SLAP tear is a a tear on the top part of the labrum that runs from the front to the back of the shoulder
The biceps tendon attaches to the shoulder to the front part of the labrum, so a SLAP tear often happens when the biceps tendon is injured.
Overhead athletes, such as baseball and softball players, swimmers, and tennis players are most commonly affected by this type of injury due to repetitive, high-energy forces exerted by the shoulder muscles, especially by the biceps tendon.
Degenerative Labral Tears In Shoulder
This type of tear occurs in people age 40 and above. With increasing age, the labrum gets frayed and its edges become rougher. Over time, a piece of the labrum may get inside the shoulder joint that can cause a clicking or a catching sensation during movement.
However, this type of tear will not typically cause pain or activity limitations.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Labral Tear In The Shoulder?
Symptoms of a labral tear in the shoulder include:
- Shoulder pain
- Shoulder instability
- Clicking or popping in the shoulder
Usually it's the pain and instability symptoms that drive people to get treatment.
Labral Tear In Shoulder Treatment
Will I Need Labral Tear Shoulder Surgery?
Surgery is the last-resort treatment for a labral tear, but for some people it's the best option.
Physical therapy is usually first-line treatment for a labral tear in the shoulder.
People who still can't perform overhead activities or compete in sports at the level that they'd like to will go on to have surgery.
Surgery most commonly needed in younger people who have had a traumatic injury to their shoulder. The acronym TUBS applies here:
- Traumatic injury
- Bankart lesion
- Unilateral - just one shoulder
- Surgery is often needed
If you're age 40 or older, surgery is NOT typically needed if you have a frayed labrum and don't participate in “high-level” physical activities.
A frayed labrum is typically addressed with physical therapy treatment focusing on improving shoulder stability and increasing pain-free function.
Labral Tear Shoulder Surgery
Labral tear shoulder surgery is typically done arthroscopically. The type of surgery will depend on the type of injury (i.e. a Bankart lesion or a SLAP tear).
Labral Tear Shoulder Surgery Recovery
The recovery timeline after labral tear surgery depends on a lot of different factors including:
- your age
- the location and severity of tear
- the surgical approach
- the surgeon’s skill level
In general though it takes about 12 weeks for the labrum to heal and 6-12 months before full recovery of the shoulder and return to activity and sports.
In general though here is a timeline for recovery after a labral repair shoulder surgery:
- 0-4 Weeks - Wearing a shoulder sling. Very little shoulder movement.
- 4-7 weeks - Start very gentle movement and muscle activation
- 7-12 weeks - gradually progress range of motion and strengthening, still in a limited range
- 12-14 weeks - recover full range of motion
- 14 to 20+ weeks - progression of strengthening and return to full activity level.
Someone who is less active will need less time to full return. Someone who is a high-level athlete will need more.
Labral Tear Shoulder Physical Therapy
Regardless of whether or not you have surgery, you'll likely need physical therapy after a labral tear.
If you don't have a traumatic injury to your shoulder and you're not a competitive athlete, chances are conservative treatment for a labral tear will probably work.
Physical therapy usually lasts 6-8 weeks. The goals of physical therapy are to improve the stability of the shoulder joint while decreasing pain and improving pain-free function.
Labral Tear Shoulder Exercises
Since the labrum provides stability to the shoulder, the goal of an exercise program should be to improve shoulder stability during arm movement, especially in an overhead position.
Shoulder strengthening and coordination exercises help to improve the stability of the shoulder.
However, it's important that you don't ONLY perform rotator cuff strengthening with your arm at your side. That's because the shoulder is most unstable when your arm is at or above should level.
Therefore, it's important to do exercises with your arm above shoulder level.
Additionally exercises to improve flexibility deficits in the chest muscles and lat muscles are also helpful.
A few simple exercises for a labral tear in the shoulder are shown in the video above.
The above exercises are a great starting point for strengthening improving coordination and stability of the shoulder joint, but watching videos on YouTube is more of a one-size-fits-some approach.
A video may work for some people, but not everyone.
If you have a labral tear in your shoulder, it's best to see an experienced physical therapist to get a program that's going to work best for YOU. That way you'll get your shoulder feeling better as quickly as possible so that you can get back to doing the things you enjoy.
If you need help for shoulder pain, tap the button below to request an appointment with a specialist physical therapist.
Like this post? Read some of our other posts about shoulder pain:
Can I Exercise With A Rotator Cuff Injury?