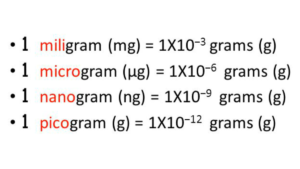Do You Feel Tired All The Time?
Do you feel sore and achy and don’t know why?
Or perhaps you've gained weight or have difficulty losing weight, even if you're dieting.
There are a number of things that can cause extreme tiredness and weight gain. However these are some of the most common symptoms of underactive thyroid in women.
Watch this video to learn:
- How to tell if you may be experiencing symptoms of hypothyroidism
- Why the your thyroid tests may come back "normal" even if there's a problem
- The proper treatment for an underactive thyroid
Chronic Pain, Extreme Fatigue, and Weight Gain Can All Be Symptoms Of Underactive Thyroid In Women
I see patients all the time who feel constantly sore, achy, and fatigued, but their doctors can't tell them what's wrong.
They may get a diagnosis of "fibromyalgia", but often that's just a label for chronic pain and fatigue with an unknown cause.
Let me reassure you:
The pain and fatigue that you feel with fibromyalgia are absolutely REAL.
However the label of fibromyalgia is often just your doctor throwing up their hands and saying “I don’t know what’s wrong. You’ve got fibromyalgia. Just deal with it.”
But patients with fibromyalgia usually have some underlying pathology causing their symptoms.
Some of the most common ones are autoimmune disorders, thyroid disorders, or autoimmune thyroid disorders such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
In this post, you'll learn:
- Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
- Causes of Hypothyroidism
- Why Symptoms of Underactive Thyroid Are More Common In Women
- Normal Thyroid Function
- Thyroid Hormone Testing
- Normal Reference Ranges For Thyroid Hormones
- Underactive Thyroid Treatment
- Thyroid Medications
- Lifestyle Changes For Hypothyroidism
Normal and abnormal thyroid function, how to tell if your thyroid may be causing your symptoms, and the next steps to take so that you can improve your energy, decrease your pain, and achieve your weight goals.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
Your thyroid gland regulates your metabolism, energy production, body temperature, and muscle and bone health.
Your thyroid levels should stay in a normal range, and if you have either too much or too little, it can cause problems.
Having too much thyroid is called hypothyroidism, which revs up your metabolism too high.
By far though, the more common problem is hypothyroidism, having too little thyroid hormone.
Symptoms of hypothyroidism can include:
- Extreme tiredness
- Weight gain
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle aches
- Joint pain
- Feeling cold all the time
- Dry skin
- Hair loss
- Depression
- Mood swings
Causes of Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism can be caused by various factors, but one of the most common is an autoimmune condition called Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
Other causes include iodine deficiency, certain medications, or radiation therapy.
Why Symptoms of Underactive Thyroid Are Common In Women
1 out of 8 women will suffer from a thyroid disorder in her lifetime, according to the American Thyroid Association.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause make hypothyroidism 5-8 times more common in women than in men, although men can get it as well.
Women are also more likely to develop autoimmune disorders in general such as Hashimoto’s disease.
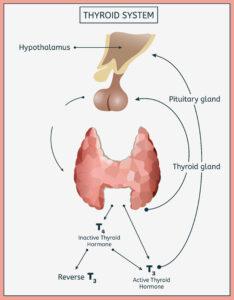
Normal Thyroid Function
Understanding how the thyroid works is crucial to getting a proper diagnosis and treatment.
Your thyroid is controlled by a region of your brain called the hypothalamus as well as your pituitary gland, which is your body’s “master gland”.
Your hypothalamus releases thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH).
TRH then stimulates your pituitary gland to release thyrotropin, otherwise known as thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
TSH stimulates your thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormone.
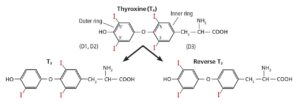
Your thyroid hormones are T3 and T4, corresponding to the number of iodine atoms the molecule contains.
T3 is the active form of thyroid hormone, but your body produces much more T4 than T3, on the order of 100 times as much.
Fortunately, your body can convert T4 into T3 by dropping an iodine molecule.
However, depending on WHICH iodine molecule gets dropped, T4 can also convert into Reverse T3, an inactive form of thyroid hormone that competes for the same receptor as T3 but without having an effect. So basically it blocks active T3 from working.
Normally, T4 gets converted to T3, but during times of stress or illness, your body favors conversion to Reverse T3 in order in order to conserve energy.
Thyroid hormone affects almost all systems of the body, but particularly the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, digestive system, and musculoskeletal system.
So it’s no wonder that when your thyroid isn’t functioning properly that it can create a whole host of problems.
Why Your Thyroid Tests Might Come Back "Normal"
The most common tests used to monitor thyroid function are TSH and T4 blood tests.
Typically if your TSH is high, and your T4 is normal, you’re considered to have sub-clinical hypothyroidism, meaning that your thyroid can produce enough hormone if your pituitary secretes more than the normal amount of TSH.
If your TSH is high and your T4 is low, that’s considered clinical hypothyroidism. That means your thyroid can’t produce enough hormone to stay in the normal range even if your pituitary is over-producing TSH.
Imagine this though:
You go to the doctor complaining of extreme tiredness and weight gain. You've searched online and you're sure that after what you've read, that you have symptoms of underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism).
Your doctor orders thyroid tests, the tests come back normal, and your doctor tells you your thyroid is fine.
But you know that your extreme fatigue and weight gain are NOT normal. Something MUST be wrong even when the test says you’re “fine”.
Get More Thorough Thyroid Testing
That's why it's essential to get a complete thyroid panel, including TSH, free T3, free T4, thyroglobulin antibodies, and thyroid peroxidase antibodies.
Free T3 and Free T4 Tests
Free T3 and Free T4 are the amounts of unbound thyroid hormone available to be used by your body.
Furthermore, it’s really the Free T3 that matters because that’s the active form of thyroid hormone.
If not enough T4 is getting converted into T3 or if too much is getting converted into Reverse T3, then you may still have symptoms, even if your TSH and T4 levels test normal.
Reverse T3 Testing
This is where a Reverse T3 test can come in handy.
The absolute level of Reverse T3 isn’t all that important.
But when you compare the Free T3 to Reverse T3 ratio, the ratio should be higher than 10. However, most functional medicine doctors prefer it to be higher than 20.
A higher ratio means you don’t have too much inactive Reverse T3 competing with active T3 for the same receptor.
Note that the units in this ratio are important as Free T3 should be in picograms per deciliter (pg/dL) while Reverse T3 is in nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL).
These are trillionths and billionths of a gram per 100 ml respectively.
So you can see how rather small variances in levels can make a big difference.
Thyroid Antibody Testing
Furthermore, thyroid antibody testing such as Thyroid antibody testing such as
Thyroglobulin Antibodies (TgAb) and Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPOAb) can give you more insight into the problem.
These antibodies recognize certain thyroid proteins as foreign and start to attack them.
Elevated levels of these antibodies can indicate autoimmune thyroid conditions, like Hashimoto's thyroiditis or Graves disease. They may also be elevated in the case of thyroid cancer.
Where To Get Your Thyroid Tested
If you're having symptoms of underactive thyroid such as extreme tiredness and weight gain, talk to your doctor about getting your thyroid tested.
A thorough thyroid panel should include TSH, Free T4, Free T3, Thyroglobulin Antibodies (TgAb) and Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPOAb), and Reverse T3.
If your doctor won’t prescribe the tests (or your insurance won't pay for them) you can also buy the tests online on your own at YourLabWork.com using the links below:
Thyroid Bundle: TSH, Free T4, Free T3, TgAb, and TPOAb
and
Reverse T3 (Specialty Test)
For full disclosure, these are affiliate links, but I think their motto of “Become Your Own Health Detective" is very applicable in this case.
You’ve got to be your own advocate when it comes to your health, and sometimes that means taking control of your health into your own hands.
Note: If you choose to order through them, they partner with Quest Diagnostics for the actual lab draw, so make sure there’s a Quest Diagnostics Lab near you.
Regardless of where you get your testing done, what do you do next?
Normal Reference Ranges For Thyroid Hormones
When you get your results, your lab results will come with a normal range or reference range. These values can vary from lab to lab.
Here are some sample reference range values, but make sure to use the range from the lab where you get tested.
- TSH: 0.4-4.5 mIU/mL
- Total T4: 4.5-12.5 ug/d
- Free T4: 0.8-2.0 ng/dL
- Total T3: 80-215 ng/dL
- Free T3: 1.5-6.0 pg/mL
- TPO Ab: <34 IU/mL
- Tg Ab: <1.0 IU/mL
- Reverse T3: 9 – 21 ng/dL
If you test your thyroid repeatedly to monitor treatment, try to get tested at the same lab each time so you’re "comparing apples to apples" so to speak.
Note: Interpretation of what the results mean is typically best done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Underactive Thyroid Treatment
So what do you do if you have your testing done and you find out that you do have an underactive thyroid?
Treatment options include medication both medication and lifestyle changes.
Some people can manage their condition with lifestyle changes alone. Others need to take medications. Either way though, making the right lifestyle changes can substantially reduce how much medication you need.
Thyroid Medication
The typical medical management of hypothyroidism is taking synthetic T4 (levothyroxine or Synthroid).
However, if your body doesn’t convert the T4 to T3, then no matter how much T4 you take, it won’t convert into the active T4.
So why not just take the active form of T3?
Well, there is such a drug called triiodothyronine (Cytomel).
Many doctors prefer not to prescribe T3 because it’s so potent. Since it’s the active form of thyroid hormone, dosage has to be carefully controlled to avoid causing hyperthyroidism symptoms. These may include palpitations, sweating, insomnia, and heat intolerance. Severe adverse reactions may include an increased risk of heart failure or stroke.
Bioidentical Thyroid Medication
Another option is bioidentical thyroid medication made from animal thyroid hormones such as Armour Thyroid. Thes may be considered for patients who don't respond well to synthetic T4-only medications.
Disclaimer: This post is just to give you information, not to tell you what medicines you should or should not take. Talk to your doctor about what will work best for you.
Lifestyle Changes For Hypothyroidism
Treatment shouldn’t just stop at medication though.
In fact, changing lifestyle factors such as proper diet, exercise, stress management, and sleep hygiene can greatly reduce how much medication you need.
Healthy diet
Eat a healthy diet making sure to get enough lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables.
Limit processed foods
Minimize or avoid highly processed foods, as they may contain additives that can affect thyroid function.
Limit gluten, dairy and soy
While these aren’t triggers for everyone, these are foods to which people have common food sensitivities. Try limiting them in your diet for a brief period of time and see if you notice a change.
Limit cruciferous vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables (e.g., broccoli, cabbage), may interfere with thyroid function when consumed in large quantities.
Exercise
Engage in regular physical activity to support metabolism and energy levels as well as to manage stress.
Stress management
Chronic stress can impact thyroid function. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, or mindfulness.
Practice good sleep hygiene
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night
- Keep your bedroom cold and dark
- Keep electronics, TVs, and work out of the bedroom so that your brain associates your bedroom with sleep.
- Try to set a consistent sleep and wake schedule
- Get 20 minutes of pre-noon sunlight per day to help circadian rhythms.
- Wind down with relaxing activities the last hour before bed-time and avoid blue light.
Limit alcohol and caffeine
Excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption can disrupt sleep and stress levels. Try to avoid drinking caffeine after noon to help you sleep better.
Stay hydrated
Drink plenty of water to support overall health. All of the chemical reactions in your body happen in water, so make sure you’re giving yourself enough of it.
Conclusion
So hopefully you found this post helpful to better understand your thyroid function and to understand if your thyroid causing your pain, extreme tiredness and weight gain.
At More 4 Life, our goal is to help people stay active, mobile, and healthy without relying on unnecessary medication, injections, or surgery.
If you live in the St. Louis area and need help for chronic pain and fatigue that you haven’t been able to figure out, tap the button below to request an appointment with one of our specialists.