If you have groin pain, it can be incredibly concerning. You may be worried about hernia or a problem with your reproductive organs. But most causes of groin pain are NOT serious.
Watch the video to learn causes of groin pain in women and men, plus stretches and exercises that can help.

In this article, you'll learn:
- What Is The Groin Pain Area?
- Groin Pain In Women
- Groin Pain In Men
- Groin Pain From Hip
- Groin Pain From Muscle
- Groin Pain Stretches
- Other Groin Pain Exercises
- How To Tell What's Causing Your Groin Pain
What Is The Groin Pain Area?
The groin area is the region between the abdomen and the thigh, where the torso meets the leg.
When people say they have groin pain they may be referring to several different areas. Some people may mean abdominal or pelvic pain, some may mean genital pain, and others may mean inner thigh pain.
So first narrowing down the exact area of the groin pain can help you figure out what's causing it.
Groin Pain In Women
Women can experience groin pain due to specific factors related to their reproductive system. While these aren't the most common causes of groin pain, they're worth ruling out.
Some potential causes of groin pain in women include:
1. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs, usually caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It can lead to groin pain, lower abdominal discomfort, and other symptoms.
2. Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or within the ovaries. They can cause pain in the lower abdomen and groin area, especially if they rupture or become twisted. Treatment options depend on the size and type of cyst.
3. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it, often affecting the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
This can result in chronic pelvic pain and groin discomfort, particularly during menstruation. Treatment may involve medications, hormonal therapy, or surgery.
4. Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids, also known as leiomyomas, are noncancerous growths that develop in the muscular walls of the uterus.
Uterine fibroids can vary in size, ranging from small, undetectable nodules to larger masses that can distort the shape and size of the uterus.
While the exact cause of fibroid formation is not fully understood, hormonal factors, particularly estrogen and progesterone, play a significant role in their growth.
Symptoms of uterine fibroids can include heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain or pressure, frequent urination, and reproductive issues.
4. Pubic Symphysis Dysfunction
During pregnancy, hormonal changes and increased pressure on the pelvis can result in groin pain.
One common condition is pubic symphysis dysfunction.
The pubic symphysis is a fibrocartilage disc that joins the two side of the pelvis in the front.
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause increased laxity the pubic symphysis causing it to stretch more than it normally would.
Wearing an SI belt or maternity belt can be helpful for treating pubic symphysis dysfunction.
ChongErfei Pregnancy Belly Band Maternit...
24% OffAdditionally, strengthening the lower abdominals and pelvic floor muscles is also helpful.
Groin Pain In Males
Men can also experience groin pain caused by various factors, including:
1. Testicular Conditions
Issues related to the testicles can lead to groin pain in men. Some possible causes include:
- Testicular torsion
- Epididymitis
- Orchitis
These conditions require immediate medical attention.
2. Inguinal Hernia
An inguinal hernia occurs when a part of the intestine or abdominal tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall.
This can cause pain and discomfort in the groin area.
Although inguinal hernias can happen in women. However, inguinal hernias are a much common in males because the inguinal canal is larger in males than females.
Surgery is typically required to treat an inguinal hernia.
Groin Pain From Hip
Groin pain can also originate from the hip joint. Some potential causes include:
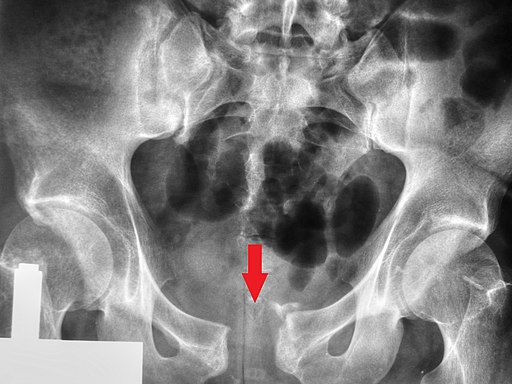
1. Groin Pain From Hip Arthritis
Hip Arthritis is one of the most common musculoskeletal causes of groin pain in both women and men over the age of 50.
When the cartilage in the hip joint starts to thin, you may experience pain when standing or walking for long periods of time. You may notice groin pain or limited mobility when bending down to put on your socks, or difficulty standing up from a low chair.
Check out these hip arthritis exercises to relieve groin pain from hip arthritis.
2. Groin Pain From Hip Labral Tear
The labrum is a rim of cartilage that surrounds the hip joint and helps deepen the hip socket.
Symptoms of a hip labral tear can vary from person to person, but commonly include groin pain, clicking, snapping, or popping in the hip, limited range of motion, or a feeling of instability.
3. Groin Pain From Femoroacetabular Impingement
Femoroacetabular impingement is another cause of groin pain from the hip joint.
This can happen due to an abnormality in either the ball of the hip joint, the socket of the hip joint, or both.
Additionally, stiffness in the back part of the hip joint can cause the ball to glide forward in the hip joint, which can create a functional impingement in the hip.
Learn how to improve hip mobility and relieve pain from hip impingement.
Groin Pain From Muscles
Groin pain can also come from the muscles and tendons in the groin area. Some common causes include:
1. Groin Pain From Muscle Strains
Overuse, sudden movements, or sports-related activities can lead to strains of your hip flexor or inner thigh muscles.
There are several muscle groups that run through the groin area including:
Hip Adductors - move your thigh toward midline
- Pectineus
- Adductor brevis
- Adductor longus
- Adductor magnus
- Gracilis
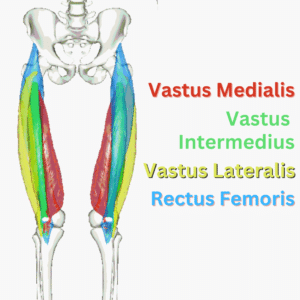
Hip Flexors
- Iliopsoas (iliacus + psoas)
- Rectus femoris (shown below)
It's important to note a muscle strain means a muscle has been overstretched or torn.
Therefore, it's NOT a good idea to stretch your groin muscles if you have groin pain from a muscle strain.
2. Groin Pain From Athletic Pubalgia
Athletic pubalgia, also known as sports hernia, is another condition that can cause groin pain in athletes.
A sports hernia is not an actual hernia like an inguinal hernia.
It's caused by repetitive twisting, turning, and excessive stress on the muscles and tendons in the groin area.
These may include the adductors, the rectus femoris (particularly in soccer players), or lower abdominal muscles.
Since athletic pubalgia is a largely an overuse injury, treatment needs to focus on activity modification, core strengthening, and proper stretching of muscles that are too stiff.
Groin Pain Stretches
Stretching exercises can be beneficial in preventing and treating groin pain.
Here are some stretches that may help:
1. Standing Groin Stretch
Stand upright with your feet shoulder-width apart.
Take a wide step to the side, keeping your toes pointing forward.
Shift your body weight to the side and lower your body by bending the knee of the leg that is stepping out.
You should feel a stretch in the inner thigh of the leg that is straight.
Hold the stretch for about 30 seconds.
2. Butterfly Groin Stretch
Sit on the ground with your knees bent and the soles of your feet together.
Hold onto your ankles and gently press your knees downward using your elbows.
You should feel a stretch in the groin area.
Hold for 30 seconds.
Other Groin Pain Exercises
In addition to stretching exercises, it's also a good idea to do strengthening exercises for groin pain.
If you've been to the gym and seen the hip adductor and abductor machine, it's tempting to think that these machines may be helpful if you have groin pain.
However, in most cases there are better options.
Hip Adduction Exercise Machine
With a hip adduction machine, you sit with the pads between your knees and use your hip adductor muscles to push the pads together.
This does strengthen your groin muscles.
However, if you have a groin strain (overstretched or torn muscles) contracting those muscles against resistance may cause further injury or tearing, at least in the early stages.
If you have stiff, tight groin muscles, then you probably need to be stretching rather than strengthening.
So the hip adductor machine is of limited value when dealing with goin pain.
I will say that the one instance I have found this to be useful is if you set the weight really light and set the pads wide apart.
Rather than using it as a strengthening exercise, in this case you allow your legs to spread wide. This allows the machine to stretch your groin muscles, kind of like the butterfly stretch mentioned above.
Hip Abductor Exercise Machine
If your groin muscles are stiff and tight, it's likely that you hip abductors may be weak. This is a particularly common finding in people with groin pain.
The hip abductor machine is one way to strengthen your hip abductor muscles.
However, there are better, more functional exercises to strengthen these muscles as well.
Single Leg Balance Exercise
You need to be able to balance yourself on one leg when walking and running. If your outer hip muscles (hip abductors) are weak, it can cause a pelvic drop when walking.
To prevent that, standing on one leg and balancing is a good exercise to start with. Make sure to keep your pelvis level
Single Leg Mini-Squat
Once standing on one leg gets pretty easy, you can progress to doing single leg mini-squats.
Make sure that you keep your knee over your toe and pelvis level when doing this exercise
Lunges
Lunges are another good hip strengthening exercise.
Keep most of your weight during the lunge on your front heel. Additionally, make sure that you don't allow your knee to drift inward.
How To Tell What's Causing Your Groin Pain
So now that you have all of these different causes of groin pain, how do you know whether exercises will help your groin pain, or if it's coming from an internal cause?
Here are some factors to consider when differentiating between the two:
1. Location and Nature of Pain
Groin pain from an internal cause, such as gynecological issues in women or testicular conditions in men, may be accompanied by other specific symptoms related to the reproductive system.
Additionally, if you feel unwell, have a fever, bowel or bladder problems, or unexplained weight loss, these are red flags that may be concerning.
Musculoskeletal groin pain, on the other hand, behaves very mechanically. It is often associated with activities, movement of the hip, or use of specific muscle groups.
2. Medical History and Risk Factors
If you have previous internal organ issues, a history of a hernia, known reproductive issues, or a cancer history, these are also important to keep in mind.
Talk with your healthcare provider about these for an accurate diagnosis.
3. Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination in many cases can help determine if your pain is coming from the hip joint or groin muscles, or from something else.
That's why it's important to see a professional if you're experiencing groin pain.
Conclusion
Most cases of groin pain aren't serious and come from musculoskeletal causes, but it's still a good idea to rule out the more serious issue. In many cases, stretches and exercises along with manual therapy and / or dry needling can help you relieve your hip pain and get back to the activities that you enjoy.
If you need help for groin pain, we'd be happy to help you at More 4 Life. Just tap the button below to request an appointment with one of our specialists.