Why Does My Knee Feel Tight After Surgery?
That's a common question that people wonder after having a knee replacement surgery.
If you've had a total knee replacement and it feels like there's a tight band around your knee - even months or a year after surgery - I want you to know that you're not alone.
That's a very common for people to experience a tightness sensation after a total knee replacement surgery. And most of the time, it's not due to a serious problem with your surgery.
Watch this video to learn why it feels like a tight band around your knee after a knee replacement surgery. Plus, you'll learn tips to decrease your knee stiffness.
Table of Contents
- Is It Serious If My Knee Feels Tight Months After A Knee Replacement Surgery?
- Why Does It Feel Like A Tight Band Around My Knee After Knee Replacement Surgery?
- What To Do If Your Knee Feels Tight After Knee Replacement Surgery
- Nerves Can Cause Your Knee To Feel Tight After Knee Replacement Surgery
- Tools To Help With Chronic Knee Tightness After Knee Replacement Surgery
- Reframing The Tight Band Feeling After Knee Replacement
- Conclusion

Is It Serious If My Knee Feels Tight Months After A Knee Replacement Surgery?
Many people are concerned that persistent knee tightness after a knee replacement may be a sign of a problem with their surgery.
Most of the time, that's not the case.
However, infections do happen in approximately 1-2% of knee replacements.
Signs of infection after a total knee replacement may include:
- Persistent Pain: Pain that persists or worsens over time, especially beyond the expected post-surgical period.
- Swelling: Unusual or excessive swelling around the knee joint.
- Redness and Warmth: The skin around the knee may become red and warm to the touch.
- Fever: A persistent fever, which could be a sign of a systemic infection.
- Drainage or Pus: Any discharge, pus, or fluid leaking from the surgical site.
- Severely Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the knee join due to pain and swelling.
- General Malaise: Feeling generally unwell, fatigued, or experiencing flu-like symptoms.
Make sure to alert your surgeon if you're experiencing any of these symptoms.
Barring these symptoms, there are many other more common causes of a tight knee following knee replacement surgery.
Why Does It Feel Like A Tight Band Around My Knee After Knee Replacement Surgery?
There are several different factors that contribute to the the "tight band" feeling around your knee after a knee replacement.
I'll group these causes into 4 different categories:
- Vascular
- Capsular
- Muscular
- Neurological
To understand this first you have to understand the state of your knee before you had the total knee replacement surgery.
Before Knee Replacement Surgery
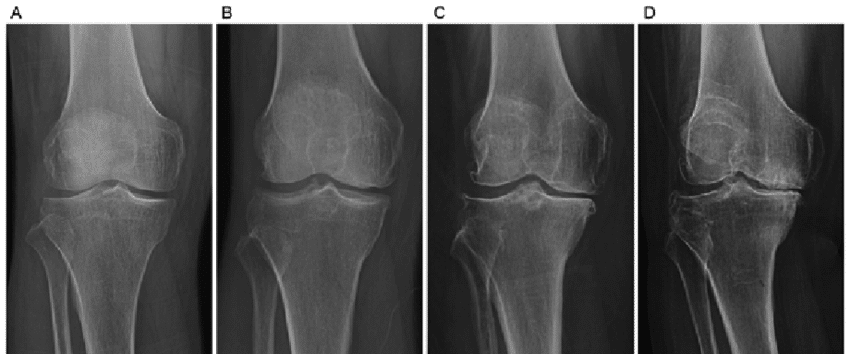
When you have knee arthritis severe enough to need a total knee replacement, you've likely lost a lot of space between the two bones in your leg.
There's also a joint capsule that surrounds your knee.
When you lose joint space, over time capsule can kind of shrink up or stiffen up.
Additionally, people who have knee arthritis have a lower density of lymphatic vessels as compared to people without knee arthritis. lymphatic vessels are what help absorb swelling and get it back into your bloodstream.
Tight Band Feeling After Knee Replacement Surgery
Now, fast forward to the total knee replacement surgery:
Your surgeon goes inside the knee joint capsule, cuts off bones, and drives metal spikes into your bones.
All of this creates a significant amount of bleeding and swelling.
Then they close the capsule back up, and now you've got more stuff inside because you've just replaced the worn-down cartilage.
Additionally, you still have all of the swelling from the surgical procedure itself. That creates even more pressure inside the knee joint capsule
Furthermore, because you still don't have a great lymph vessel density in the capsule, it's a lot harder to reabsorb that swelling.
In fact, some people continue to have persistent swelling for months or even years after a total knee replacement.
Your replaced knee may never go back down to the size of the other one, and that's okay.
That doesn't necessarily indicate that there's an issue with your surgery or that something's wrong inside the knee.
It's just the nature of the beast (knee replacement surgery).
However, there are some things you can do to decrease how tight your knee feels after surgery.
What To Do If Your Knee Feels Tight After Knee Replacement Surgery
Right after knee replacement surgery, it's important to get your knee moving as quickly as possible.
If you're reading this either considering having a knee replacement or you've recently had a knee replacement, it's important to do your therapy right away.
Starting to move your knee shortly after surgery helps move fluid within the joint capsule.
It also helps prevent the bleeding from the surgery from forming scar tissue in the knee joint capsule.
So, the quicker you get moving after your knee replacement, the less likely it is that you'll experience persistent knee tightness.
But even if you do everything right, some people still experience a tight band feeling around their knee for months after surgery.
We mentioned the vascular and the capsular components already, but you've also got some muscles around your knee that can contribute to knee stiffness.
When you have total knee replacement, your surgeon replaces the joint surfaces, but they don't replace the muscles around your knee.
It's likely that these muscles have become stiff even before surgery.
Then when you have traumatic "injury" to your knee such as a surgery, your muscles further stiffen up to protect your knee against further "damage".
There was a randomized controlled trial in which patients either received trigger point dry needling or sham dry needling right before having a knee replacement while they were under anesthesia.
The study found that the dry needling group experienced less pain in the first month following knee replacement surgery, when the pain is the most severe.
And because they were asleep, the patients didn't know whether they received it or not. Therefore, the change couldn't have been due to placebo.
Furthermore in a case series of 14 patients with persistent (6 months) knee pain after knee replacement, dry needling helped improve knee pain, stiffness, range of motion, and walking distance.
These studies both go to show that muscular trigger points can contribute to pain and stiffness after knee replacement surgery.
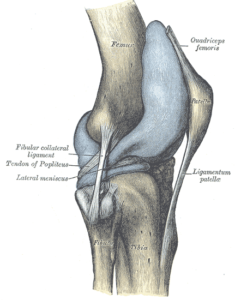
Additionally there's a muscle around the back of your called the popliteus.
A recent systematic review has identified that popliteus tendon impingement can also be a cause of persistent knee pain after a knee replacement surgery.
The function of the popliteus muscle before you have a knee replacement is to unlock the knee when you start to bend it.
That function isn't quite as vital once you've replaced the joint surfaces because of the design of modern prosthetic knees.
The popliteus tendon can get injured during surgery, or it can get impinged or "pinched" inside the joint.
Thus, the popliteus can create a feeling of a tight band around the knee.
Because that's essentially what it is.
Although the popliteus isn't as necessary in an artificial knee as a real knee, it is important to consider that rotational component of your tibia during your rehab process.
This isn't something that you'll want to start right after surgery because you still want to give the implant good time to settle in to the bone before your start twisting your knee.
But if you're several months after knee replacement surgery, there are going to be times in life when you're going to have to pivot and twist.
Your physical therapist can help you restore the rotational mobility of your knee using manual therapy techniques.
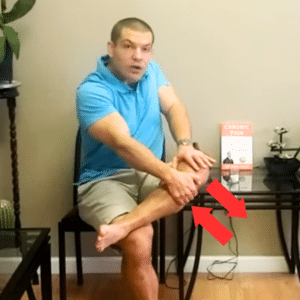
You can also do a technique at home where you cross the ankle of your surgical leg over the opposite knee.
Then gently push your thigh outward while pulling your tibia inward.
This is just a very slight glide - millimeters of motion.
You don't want to be overly aggressive with it. You just want to restore the normal rotational mobility of your knee joint.
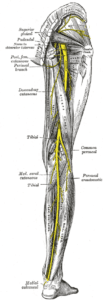
Nerves Can Cause Your Knee To Feel Tight After Knee Replacement Surgery
The nerves around your knee can also make your knee feel tight after a knee replacement surgery.
The sciatic nerve runs down the back of your knee, and then it splits into a tibial branch and a fibular branch right behind the knee.
Then those further branch into what are called genicular nerves, which supply the actual knee joint itself.
Those nerves can get nicked or irritated during the surgery.
Sometimes patients will even complain that they have a little bit of numbness around their knee. Often that feeling will improve over time, but sometimes it doesn't go away completely.
In any case, after surgery, those nerves get hypersensitive and irritable.
They're still trying to figure out what the "new normal" is with the knee.
Because a knee replacement isn't exactly like your natural knee.
So they may send your brain some altered sensations telling it that your knee feels tighter than it used to be until they figure out that this is the new "baseline" tension level of the knee ligaments and joint capsule.
So those were the four causes of that tightness or band-like sensation around the knee.
Again those were vascular, capsular, muscular, and neurological.
Next, I'll share some tips that can help improve the feeling of tightness around the knee after knee replacement.
Tools To Help With Chronic Knee Tightness After Knee Replacement Surgery
There are some relatively inexpensive tools and devices that you can buy to help with post knee replacement tightness.
Instrument Assisted Soft Tissue Mobilization (IASTM)
One of the things that I found works great clinically is doing instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization.
The most common methods used are Graston Technique® (metal tools) or Astym® therapy (plastic tools).
These are proprietary techniques used by physical therapists and chiropractors.
However, instrument assisted soft tissue mobilization has been used for thousands of years.
Gua Sha tools, originally made out of stones, have been used back since ancient Chinese times.
Hana Emi Gua Sha Facial Tools (Set of 4)...
20% OffEssentially, you take something with sort of a sharp-ish edge (not sharp enough to cut you), and you just run it along your skin.
People will often describe this as "scraping".
But you don't want to scrape really hard to the point where you see bruises on your leg.
There are people who will go to physical therapy and get this treatment from well-meaning clinicians and come back just incredibly bruised.
The purpose of IASTM is not to mechanically "break up knots", but rather to stimulate a healing response.
The edge of the tool catches on little adhesions in your muscles, ligaments, or joint capsule.
It breaks up small, nonfunctional capillaries and stimulates a cellular response in which your body eats up old unhealthy tissue and replaces it with newer, healthier tissue.
It's good to use IASTM around the kneecap, kind of over the ligaments around the knee, and on the patellar tendon on the calf muscles and thigh muscles.
Using this on all different areas of the knee can be helpful to help restore more of that tissue mobility.
If you are going to use IASTM, just make sure that your surgical incision is well healed. Don't do this over a fresh scar that hasn't closed up well. If you have concerns, see a physical therapist to get treatment instead of doing it yourself.
Exercise Biking
Exercise biking can help with the post-surgical healing and remodeling process.
Whether you use it at physical therapy or go to a gym or have one in your home, using an exercise bike is really helpful.
Having an exercise bike at home can be good though because the more convenient it is for you to do it, the more often you're likely to actually do it.
Schwinn Fitness 230 Recumbent Bike
14% OffExercise biking can help:
- mechanically move fluid around inside the joint capsule.
- stimulate remodeling of the joint capsule and post-surgical scar tissue.
- increases blood flow and circulation which will help flush some of that swelling and bring nutrients to the area
So using an exercise bike is another really helpful tool if your knee feels stiff or tight after a knee replacement surgery.
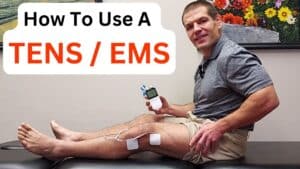
TENS / EMS Units
A TENS / EMS unit can also help if your knee feels tight after a total knee replacement.
NURSAL Dual Channel TENS Unit Muscle Sti...
22% OffWhile TENS doesn't mechanically do anything, it can help neurologically decrease sensation of tightness.
When you use a TENS unit, your brain picks up on that tingling or vibration from the TENS unit rather than the tightness sensation.
Additionally, if you have an Electrical Muscular Stimulation (EMS) function on your TENS unit, you can use it to create a rhythmic muscle contraction.
That functions as a lymphatic pump to help move fluid away from the knee.
Exercise does the same thing, but you can use a TENS unit at rest.
Check out this post about how to use a TENS / EMS unit.
Massage Guns
Finally, you can use a massage gun to help with knee tightness after a knee replacement.
BOB AND BRAD X6 Pro Massage Gun Deep Tis...
$139.99 (as of April 28, 2024 02:29 GMT -05:00 - More infoProduct prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.)10% OFF Discount Code: JAH3HED8
This helps decrease stiffness in the muscles around the knee, particularly the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves.
I wouldn't recommend using a massage gun on the popliteus. Your sciatic/tibial nerve are located right in the back of your knee and you don't want to irritate them with a massage gun.
However, just you can use your fingers to gently massage the soft area in the back of your knee (popliteal fossa).
Save 10% OFF the Bob & Brad X6 Pro Massage Gun
Use Discount Code: JAH3HED8
Reframing The Tight Band Feeling After Knee Replacement
One last tool that you can use if you have tightness around your knee after a knee replacement is a cognitive technique known as reframing.
That's essentially just altering the way that you think about it.
If you think about it as a "problem", something that needs to be addressed, then your, then your brain is going to see the knee tightness as a potential danger.
The International Association for the Study of Pain describes pain as:
"An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage."
Whether the tightness actually hurts or whether it's just bothersome, if you view it as unpleasant and you're worried that it may indicate a problem, your brain is going to pay attention to it.
Your brain is going to tell your nerves to send it lots of information about the "problem" so it can make sure the problem doesn't get worse.
This type of thinking might include self talk like:
- Why is this happening to me?
- What's wrong?
- Has something gone wrong with my surgery?
However if you think about the tightness as as just a normal feeling that people have after a knee replacement surgery, your brain won't focus in on it so much.
In fact, knee tightness usually doesn't indicate an infection or other problem with you your knee surgery.
Your nerves may just need to adapt to the fact that your new artificial knee is different from your old knee.
It's going to feel different, but in time that "different" will be the the new normal.
Furthermore, some of the tips mentioned in this post give you some level of control over the tightness sensation.
When you have control over something, your brain worries less than when you lack control.
And if your brain isn't worried about it, it's not going to ask your nerves to send as much information about the situation.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this post helped give you some peace of mind to know that if it feels like there's a tight band around your knee after a knee replacement surgery, that's very common and likely doesn't indicate a problem with your surgery.
Furthermore. hopefully you learned some tips to help give you control over that tight knee feeling.
If you live in the St. Louis area and need more help for persistent pain or tightness after a knee replacement (even if it's been months or years), tap the button below to request an appointment with one of our specialist physical therapists.
Like this post? Here are some others you may enjoy:
Top 5 Mistakes After Knee Replacement
Top 10 Reasons For Chronic Pain After Knee Replacement
How To Walk Without A Limp (Even With Arthritis Or After Hip Or Knee Surgery)
Total Solutions For Total Knee Replacement with guest Tony Maritato